Ethernet vs fiber optic cables: what’s the difference and how do they work?
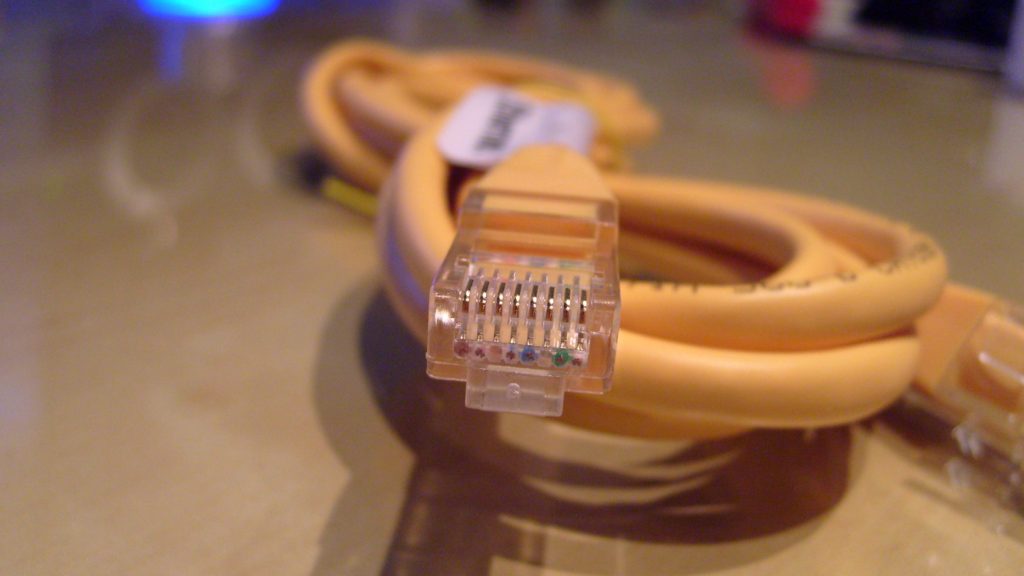

Image: DeclanTM | Flickr
The internet has become critical for communicating and doing business in the modern world. The availability of sufficiently high-speed Internet can profoundly influence economic growth in a community or a nation.
Other than wireless, there are two primary ways data bandwidth can be transmitted to our homes and businesses:: through Ethernet cables containing copper wires transmitting data with electrical impulses and through fiber optic cables transmitting data using light.
What are the differences between Ethernet cable and fiber optic cable for transmitting data over the Internet? And how much faster is Fiber optics? We put together this guide to answer those questions and more.
Ethernet Cables
The Ethernet standard has been around for quite some time now. It was first developed by Xerox in the 1970s and was introduced commercially in 1980. Ethernet uses copper cables to deliver data using electrical impulse, and it has a reputation of being a lot slower than fiber optic cables. This is still true but Ethernet has come a long way toward becoming a faster means of delivering Internet access.
There was a time when Ethernet speed had a 10Mbps (Megabits per second) limit. Now, however, “fast Ethernet” offers rates of up to 100Mbps, while Gigabit Ethernet can deliver speeds of a hefty 1000Mbps. Currently, Cat 6 Ethernet cables can carry up to a massive 10Gbps. While this is lightning fast, fiber optics are still much faster.
Ethernet cables send data through electrical impulses, and most Ethernet cables fall under Cat 5 — which uses eight individual 24-gauge copper group wires into four pairs inside the cable. In reality, copper wires transmit data pretty directly — a combination of 1s and 0s represents all data, and in copper wires, that means a variation of voltage.
Ethernet does have its drawbacks. Because it uses electrical signals, it’s both vulnerable to electromagnetic interference and data transmitted this way is vulnerable to being intercepted by hackers at the hardware level. That can be a security and privacy risk.
Also, there are inherent limits to how fast data can be transmitted over copper wires that are much lower than the inherent limits on the transmission of data using light (i.e., fiber optics).
Fiber Optics
Image: Roshan Nikam | Flickr
While fiber optic cables are a relatively new method of delivering Internet to homes and businesses, the principles behind fiber optic cables date back over 100 years.
Television cameras used on the NASA Apollo 11 mission to the moon in 1969 used fiber optic technology. These days, fiber optic cables are often used for extremely high-speed data transfer for businesses that need the bandwidth, and for transferring data over long distances.
So how do fiber optic cables work? Fiber optic cables are made up of tiny strands of pure glass that carry data through light instead of through electrical impulses. They also come in two different types — single-mode and multi-mode.
Single-mode cables use laser light to send signals, while multi-mode cables use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to send signals. As mentioned above, data is represented by a combination of 1s and 0s. In fiber optic cable that means that light is either on or off, blinking extremely fast, representing 0 when the light is off and 1 when the light is on.
Standard fiber optic cables transfer data somewhere between 10Mbps and 10Gbps, but a single strand of fiber optic cable has been proven to be able to carry data at up to an extremely fast 100 Tbps (Terabits per second),. Fiber optic cables usually include many strands, each strand multiplying the amount of data that the strand containing cable can transmit.
Fiber optic cables are also more secure than Ethernet cables, as hackers cannot intercept the data at the hardware level, protecting your data in transit.
Fiber optics can transmit more data faster and more reliably than copper wires, making for a more secure, fast, and reliable Internet for homes and businesses.
Conclusion
The differences between fiber optic and ethernet cables are numerous, and while it’s likely that eventually, fiber optic cables will become more commonplace, for now, ethernet cables are still the dominant way to transmit data. It works well as far as it goes.
Still, as data demands get higher and higher, fiber optic technology will become a critical part of the Internet infrastructure, spurring communities to deploy fiber optics to attract businesses seeking reliable, fast bandwidth that will meet the needs of growing companies.
The growth in the use of fiber optics is moving toward a day when Internet access will use fiber optics to deliver the Internet to most homes and businesses. Everyone will have lightning fast Internet delivered by fiber optic cables transmitting data securely.













One thought on “Ethernet vs fiber optic cables: what’s the difference and how do they work?”